What Are the Different Types of Auto Loans?
Car buyers have several choices in types of car loans for financing their next vehicle purchase. Some are more common than others, but it’s helpful to know about the different types of car loans that you may come across as you shop for your next vehicle.
The main differences in the types of auto loans are whether the vehicle is used as collateral, the way the interest is calculated and the source of financing. There are also special types of auto loans for special circumstances.
Below, we’ll help you decide which type of car loan best suits your financial situation.
In this article, we’ll cover…
Secured auto loans vs. unsecured auto loans
There are two types of auto loans: secured or unsecured. For a secured loan, the lender puts a lien on the vehicle that is being purchased. Other types of secured loans will put a lien on other collateral owned by the borrower, such as a house or another vehicle. If payments are not made, the lender may repossess and sell the asset to recover money to pay off the loan balance. It’s important for borrowers to understand which assets are secured by a loan and are therefore subject to repossession.
An unsecured loan, on the other hand, is not tied to any assets. If payments are missed, the lender has to pursue payment from the borrower through other legal means. That’s why unsecured loans typically come with higher fees and interest rates.
| Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|
| Secured auto loans | Lower finance charge Lower overall loan cost | Potential for asset repossession for nonpayment Asset used to secure the loan must meet lender requirements |
| Unsecured auto loans | No restrictions on how you use the money | Higher finance charge |
Secured auto loans
Secured auto loans are the most common type of car loan for new and used vehicles. The loan is secured by a lien on the vehicle, and the title can’t be transferred without satisfying or paying off the lien. If you fall behind on the payments, the lender can repossess the vehicle and sell it to recover the money owed on the loan.
Traditional auto loans: A secured auto loan is the type of car loan you will be offered by banks and credit unions. Because the loan is tied to the vehicle, secured auto loans typically have the most attractive APR rates and terms. The best interest rates go to those who have an excellent credit rating. Many auto manufacturers have captive auto financing companies — such as Ford Credit or Honda Financial Services — and offer incentive rates on new and certified pre-owned cars. Traditional auto loans can be used for:
- New cars: You’ll typically find the lowest rates for the newest cars.
- Used cars: The older the car, the higher the interest rate will probably be. “Used” could apply to a car that’s only a month old, including certified pre-owned (CPO) cars.
Balloon loans: This secured car loan has a unique payment structure. Balloon auto loans feature relatively small payments for the first few years of the loan and then a large final payment at the end, which is often thousands or even tens of thousands of dollars. When the loan “balloons,” you could make the large final payment, trade the car in for another one or sell it and pay off the loan.
Business and fleet auto loans: Businesses buy cars and trucks with commercial-level financing because the vehicles may not qualify for traditional auto loans. There are a number of options for financing business or fleet vehicles:
Unsecured auto loans
Personal loans, credit card debt, personal lines of credit and student loans are all types of unsecured debt. They aren’t linked to any asset that could be repossessed. There are fewer restrictions on how the money is used, so it could be a good option for a car that doesn’t fit the traditional mold. Review personal loan lender options with LendingTree to determine whether this is a smart financial decision.
This type of car loan could be attractive if you’re buying an inexpensive car with a price below the minimum for traditional bank financing. For example, Capital One has a $4,000 minimum for an auto loan.
An unsecured loan could also be an option if you’re buying an old car or collector car that doesn’t qualify as collateral for secured financing. Lenders often have restrictions on the age and mileage for a car to serve as collateral. Bank of America, for example, will only finance cars that are 10 model years old or newer and have less than 125,000 miles on the odometer.
Simple interest loans vs. precomputed interest auto loans
You may be offered a choice between a simple interest loan or a precomputed loan. Each type of car loan calculates interest differently, so it’s important to understand the impact of late or missed payments, as well as early payoff. In both cases, as long as you pay off the loan at the end of the full loan term, there’s usually not much difference. However, there will be a difference if you want to pay off the loan early.
| Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|
| Simple interest loans | Allows for easy reduction of interest if you repay the loan early | Large portions of your first payments go toward interest, not the principal |
| Precomputed interest loans | You pay an equal amount of interest on each payment | It’s hard to reduce the total cost of the loan |
Simple interest loans
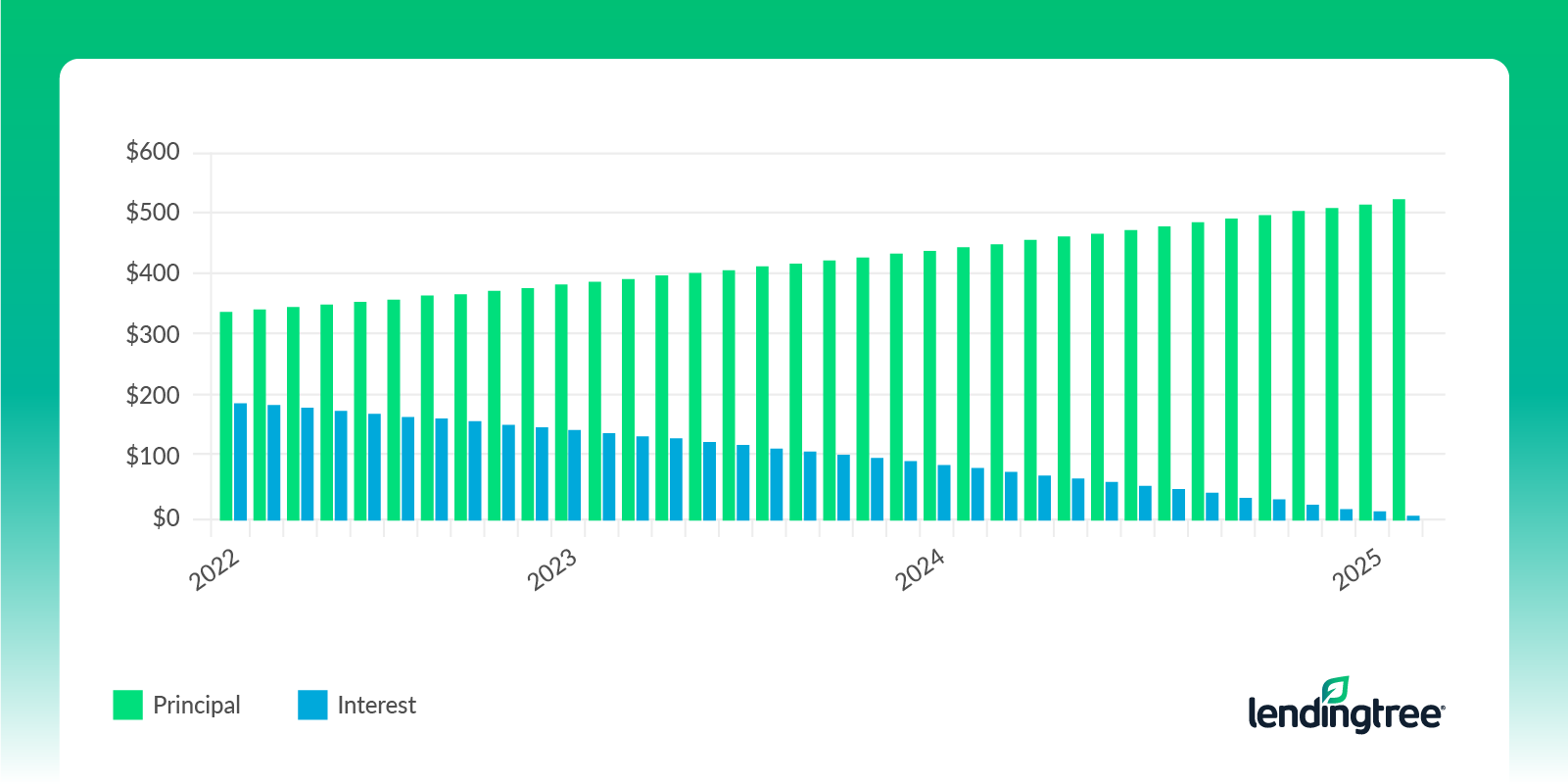
In a simple interest loan, your monthly payment is calculated based on the interest rate, the balance of the loan and the daily interest accrued since the last payment. It’s the most common type of car loan in use today. Each month, your payment first goes toward interest, and the remainder pays down the principal. As a result, a higher percentage of your monthly payment goes toward interest at the beginning of your loan, and by the end of your loan term, you’re mostly paying off the principal.
A simple interest loan allows you to make additional payments in addition to the regular monthly payment so you can pay off the loan early and save on interest charges.
In this example, the car payment is always $527.05. The amount of interest you pay (in blue) decreases with each payment you make as you pay off the principal.
Precomputed interest loans
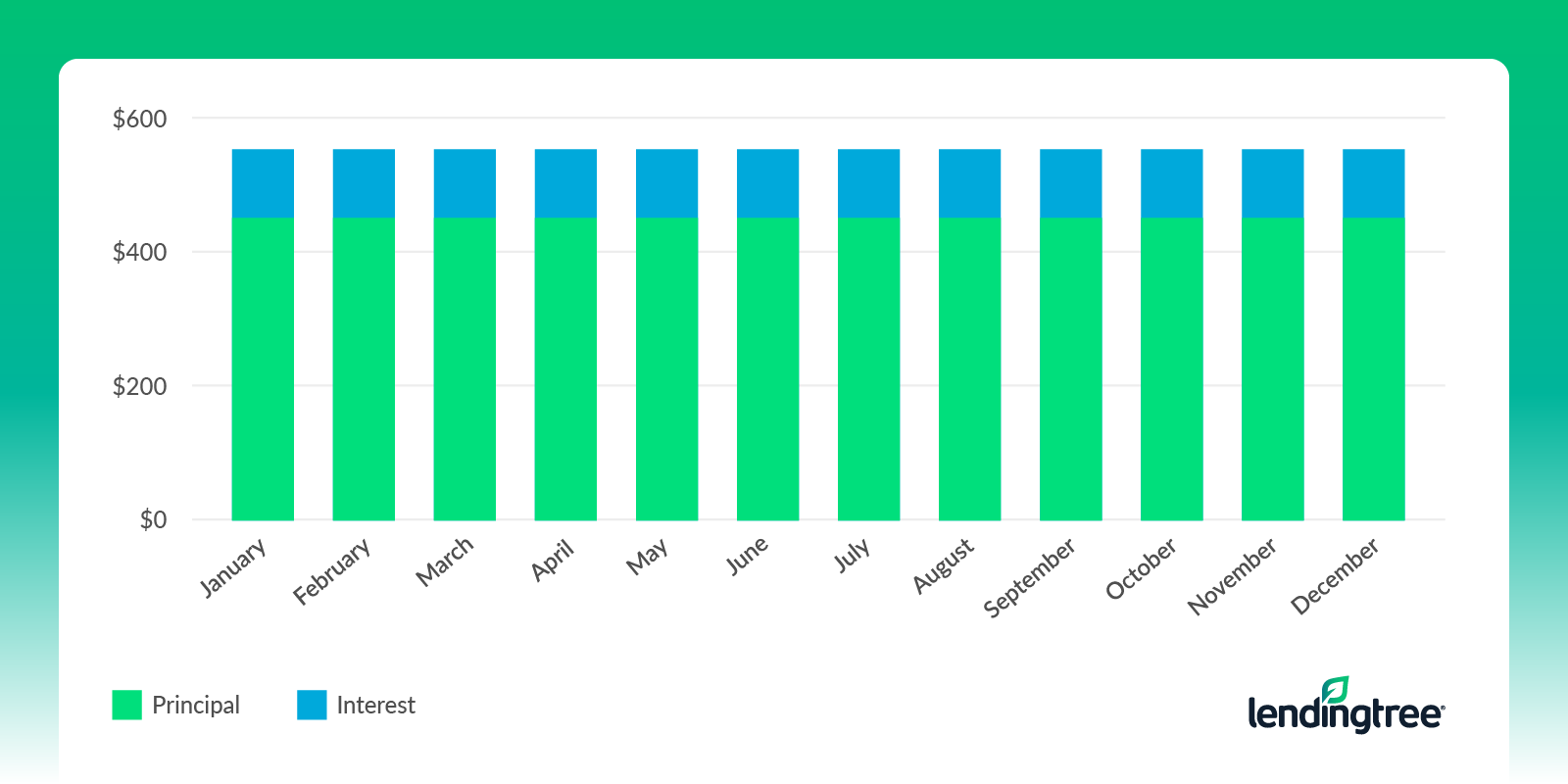
With a precomputed interest loan, the loan balance, origination fees and interest are calculated at the beginning and divided across the loan term. With this loan, borrowers enjoy a fixed monthly payment, fixed interest rate and rigid payment schedule. If you incur late payment fees, the percentage of your payment that goes toward the principal may be reduced to cover the fees. Monthly payments could be lower than a simple interest loan, but there’s no incentive to pay off the loan early.
In this example, the car payment is always $527.05. The amount of interest you pay (in blue) stays the same with each payment across the life of the loan.
Direct auto financing vs. indirect auto financing
Direct financing is when you obtain a loan by interacting directly with the lender, like a bank or credit union. Indirect financing is when there’s an intermediary between you and the lender, like a car dealership. Most consumer auto lenders are both direct and indirect lenders. You can obtain an auto loan from them by applying directly or going through a dealership. There are some pros and cons to each type of relationship.
| Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|
| Direct financing | Access to loan offers without a third party filtering the information | Separate applications for each lender can take time and effort |
| Indirect financing | Receive multiple offers by filling out one form | You may not see every offer you receive, and dealerships have the ability to raise your APR |
Direct financing
With direct financing, all communication is done directly between lender and borrower. You won’t have the dealer filtering information.
You can find direct financing through a bank, credit union or online lender. It’s often a good idea to apply to lenders directly to secure your own financing before you go to the car dealership. The interest rate you are offered will be based on your credit score and payment history. With that knowledge, you can compare the financing offers from the dealer to make sure you’re getting the best rate for you.
Indirect financing
Dealer-arranged financing is a common form of indirect financing. The dealer’s finance office can shop your application among some of the same lenders you can go to directly. It will also submit your application to its captive finance company, such as Toyota Financial Services.
While many buyers like the simplicity of indirect financing, be aware that dealers may increase customers’ APRs and pocket the difference between the rate you agree to and the rate you actually qualify for. The dealer may not always show you the best offer for your budget.
Prequalification vs. preapproval
Although prequalification and preapproval sound very similar, they are two different things. The difference is based on the lender’s commitment to providing financing for you and your level of interest in getting financing for a car loan. We highly recommend getting preapproved for an auto loan before you visit a dealership.
| Prequalification | Preapproval |
|---|---|
|
|
Prequalification is simpler and faster and is based on your annual income and how much other debt you already have. The lender may also consider your credit score to let you know if it’s likely you’ll qualify for the loan amount you are seeking. Banks will perform a soft pull on your credit for a prequalification, which won’t impact your credit score. A prequalification is not a guarantee of financing approval or an offered APR.
Preapproval represents more of a commitment from the lender that they will provide an auto loan for the amount you need. The lender reviews your credit score and verifies income and debt levels. It’s still not a guarantee you will get the loan, but it provides you and the auto seller with a high level of confidence that you will receive the financing you need. The preapproval is based on the loan amount, interest rate and loan term so you have a solid picture of what your payments will be.
A preapproval requires a hard pull or full inquiry on your credit, which could temporarily lower your credit rating by a few points. However, if you’re shopping for a car, you can have multiple hard pulls within 14 days that are treated as a single pull for your credit rating. With LendingTree, you can receive up to five car loan offers by filling out a single form.
Special types of auto loans
There are many types of loans for buying a car, not to mention refinancing a car. Sometimes, car buyers have special circumstances that require specialized loans. Here are a few common ones:
Military auto loans
Special auto loans are available to active-duty and retired service members from both direct and indirect lenders. Dealers in areas with a large military presence are often experienced in helping servicemen and servicewomen secure financing. Some credit unions with military membership, such as Navy Federal CU and PenFed credit unions, offer auto loans for military members. Many auto manufacturers offer discounts (of $500 to $1,000) on new vehicles to service members. Additionally, the Servicemembers Civil Relief Act provides protection for military members who must break a car lease due to a permanent change of station.
Buy-here-pay-here loans
These loans are typically used by people with low credit scores who aren’t able to access other types of car loans. Interest rates tend to be higher than average and the cars may be lower in quality. These loans often carry a higher risk of repossession. Since buy-here-pay-here lenders aren’t known for their competitive rates and can sometimes have predatory lending practices, we recommend considering a bad-credit auto loan instead.
Title loans
A car title loan is a loan secured by the title to the car used to get cash. Title loans often come with sky-high interest rates; in fact, the Federal Trade Commission reports that title loan lenders often charge as much as 300% APR. Plus, if you don’t pay the loan, the car can be repossessed and sold.
A secured loan with a lien against the vehicle it is financing is the most common type of auto loan.
The APR varies by your credit score, payment history and loan terms. New cars often have APR incentive offers that offer the lowest rates.
If you have a simple interest car loan, you can save interest by paying the car loan off early. As long as your loan contract doesn’t include a hefty prepayment penalty, repaying your loan early can be a good idea.


