SBA Form 413: How To Fill Out the Personal Financial Statement Form
When applying for certain loan programs backed by the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA), you’ll need to fill out SBA Form 413, which helps the SBA evaluate your financial situation. SBA-backed loans come with many benefits, including more lenient eligibility requirements and a cap on interest rates.
But the approval process takes time, and the application may seem daunting. We’ll walk you through the process of filling out the personal financial statement form step by step so you can feel confident submitting your SBA loan application.
- SBA Form 413 is required to apply for many SBA loan programs, including the popular SBA 7(a) loan.
- The form requires detailed information about your finances, so it may take some time to fill out.
- Leaving fields blank may cause your lender to question the completeness of the form, but if an asset or liability does not apply to you, you can enter $0 or N/A, depending on the section.
What is SBA Form 413?
SBA Form 413, also known as the personal financial statement, is intended to collect details about applicants’ personal finances. The Small Business Administration and approved lenders use this form to help determine a borrower’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan. All borrowers and guarantors applying for certain SBA loans must fill out SBA Form 413.
Although SBA Form 413 requires you to provide a lot of information, it offers an important snapshot of your small business finances. If you’re approved and get the funding you need, it will be well worth the effort.
If you’re applying for the Women Owned Small Business (WOSB) Federal Contracting Program or the 8(a) Business Development program, the SBA will also use the form to make sure you meet the eligibility requirements. Your net worth, income and assets must fall below each program’s threshold.
Who needs to fill out SBA Form 413?
SBA Form 413 isn’t required for SBA microloans, but it is required for most other loan programs and surety bond guarantees. You’ll also need to fill out Form 413 for the following programs:
The following individuals and entities are required to fill out the form:
- Proprietors
- General partners
- Managing LLC members
- Owners with 20% equity in the business or more
- Guarantors
For the WOSB and 8(a) programs, spouses must fill out a separate form, unless you’re legally separated.
How to fill out SBA Form 413
1. Download Form 413 from the SBA.gov website
To get started, download SBA Form 413 from the SBA website by clicking the blue button. Be sure to save your progress as you go to avoid any issues.
2. Gather required documents
Even if your SBA lender doesn’t require you to submit these documents with your application, it can be helpful to have them on hand while you’re filling out the personal financial statement form. Your financial institution will probably allow you to access many of these documents online.
- Checking and savings account statements
- Retirement account statements
- Invoices for accounts and notes receivable
- Life insurance documents for policies with cash value
- Brokerage account statements or personal investment documents
- Mortgage account statements
- Credit card statements
- Auto loan statements
- Statements of other debts, like personal loans
- Pay stubs
- Documents from any other income sources
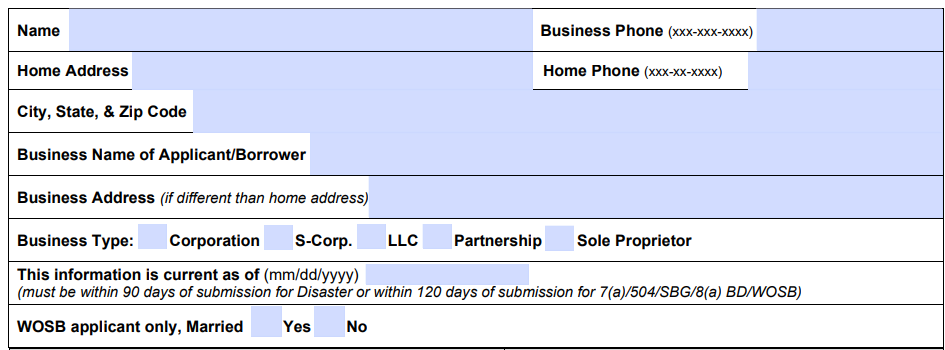
3. Fill out personal and business contact information
At the top of the form, check the box for the loan program you are applying for. On the second page, you’ll see space for your name, business address, business phone number, home address and home phone.
You’ll also need to enter your business name and check the box for the correct business type (corporation, S-corp, LLC, partnership or sole proprietor). Make sure to date the form as well. If you’re a WOSB applicant, indicate whether you’re married.
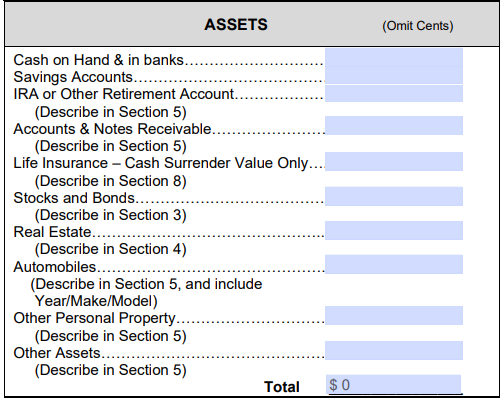
4. List your assets and calculate total value
When listing the value of your assets, round to the nearest dollar. You should include your portion of any assets you own with your spouse. For example, if you co-owned a home with your spouse, 50% of that would be yours.
You’ll need to calculate the value of the following:
- Cash on hand and in banks: Calculate the combined value across your checking accounts and any other non-savings accounts that you may have, as well as your portion of any joint accounts with your spouse.
- Saving accounts: Add up the money in your savings accounts, including your portion of joint accounts.
- IRA or other retirement accounts: Add up the balances in each of your retirement accounts.
- Accounts and notes receivable: If you have unpaid invoices, list the total amount here.
- Life insurance: If you have a life insurance policy with a cash surrender value, list the cash surrender value here.
- Stocks and bonds: List the current value of your stocks and bonds and your half of those you own jointly with your spouse. You may want to complete this section when the stock market is closed.
- Real estate: Add up your half of the present value of all the real estate you and your spouse own, including your primary residence.
- Automobiles: If you or your spouse own vehicles, add up your share of their current fair market value here.
- Other personal property: Estimate the cost of any other property you own, such as valuables like your jewelry and electronics.
- Other assets: Add the worth of anything else valuable not included above, including the value of outstanding loans you made to others.
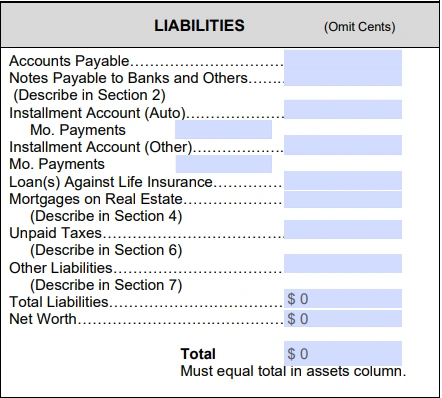
5. Add your liabilities
Next, you’ll list the amounts you owe, including your portion of debts held jointly with your spouse. You’ll need to provide information about the following, and will need to provide some additional details below:
- Accounts payable: List the value of your unpaid bills, such as money owed to vendors, not including loans with financial institutions.
- Notes payable to banks and others: Add up the value of your notes payable — this includes things like personal and student loans, or debts to banks not listed on other lines.
- Installment account (auto): Enter the outstanding balance for all auto loans on purchased vehicles. Underneath, write your monthly payment.
- Installment account (other): Add up your credit card debt and other installment account balances and enter them here, along with your total monthly payment toward these debts.
- Loans against life insurance: If you’ve taken out a loan against your life insurance policy, enter the outstanding balance due here.
- Mortgages on real estate: For all properties you and your spouse own, add up your portion of the mortgage balances.
- Unpaid taxes: If you have taxes that are currently due that you have not yet paid, enter the amount here. Don’t include expected taxes for the year that aren’t due yet.
- Other liabilities: If you have other debts you didn’t describe above, enter the total amount here.
- Net worth: To calculate your net worth, first fill in the total liabilities and total assets lines by adding the entries for each section. Next, subtract your total liabilities from your total assets and enter the result for your net worth.
SBA Form 413 is designed to tell the full story of your financial situation — but not every line applies to every borrower. For example, if you don’t own any stocks or bonds, you won’t need to report any in the Assets section of the form.
In the Assets and Liabilities sections, enter 0 for any items that don’t exist or don’t apply to you. In the detailed sections that follow, type “None” or “N/A” to tell your lender that these items were not skipped by mistake. For instance, if you don’t have any unpaid taxes, you can write “None” in Section 6.
6. List sources of income
- Salary: Add up your total salary from your business in addition to other employment.
- Net investment income: Add up your total dividends, interest and other investment income.
- Real estate income: Provide your total income, after expenses, earned through selling or renting your real estate properties.
- Other income: If you receive alimony, Social Security, a pension or any other source of income not listed above, put the total on this line.
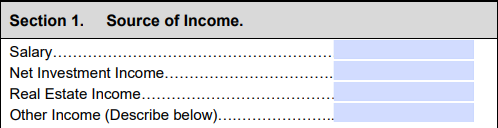
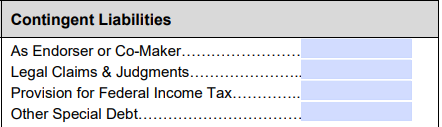
7. List any contingent liabilities
Contingent liabilities are, essentially, potential debts. You won’t owe any money, and they won’t count against your total net worth unless a specific event occurs. If you have any of the following, put the total amount in this section.
- As endorser or co-maker: If you’ve cosigned on any loans or credit cards, enter the total potential debt you could be responsible for if the main borrower defaults.
- Legal claims and judgments: If you’re the defendant in a lawsuit and could be responsible for any judgments, enter the potential total here.
- Provisions for federal income tax: If you’re planning to sell an asset or may incur other tax liabilities, enter the potential total here.
- Other special debt: If there are other contingent liabilities you haven’t listed above, put the total on this line.
8. Share additional information about assets and liabilities
The rest of the form asks you to provide additional information about your assets and liabilities, which you listed the dollar amounts for in previous sections. Here’s what you’ll need to describe.
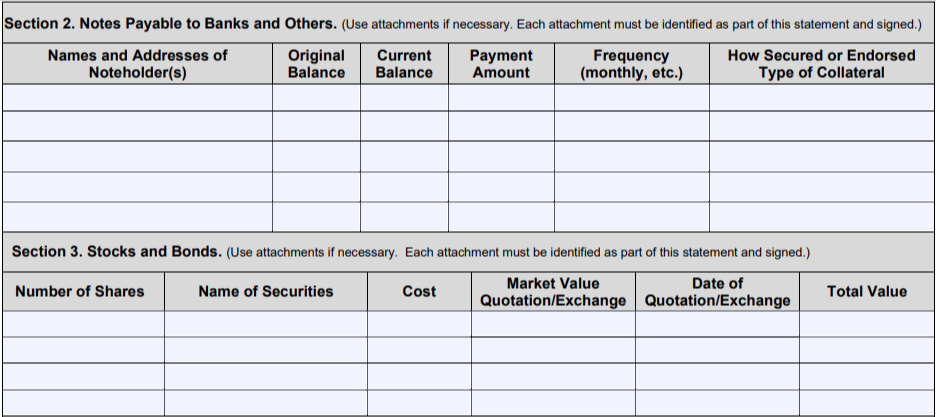
- Section 2: Fill out the details for each note payable to banks and others, not including mortgages.
- Section 3: Not including stock in your business, enter the details for all shares of stocks and bonds you hold. You may want to attach financial statements from your brokerage accounts.
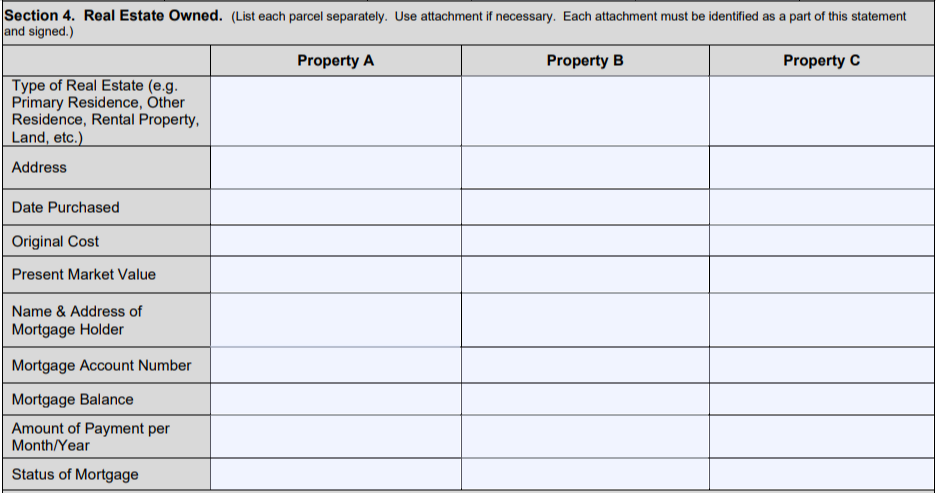
- Section 4: List your primary residence, if you own a residence, in the top field of the “Property A” column and fill in the details below. Do the same for your other properties, and identify what type of real estate it is. Make sure the values correspond with what you have listed in the assets and liabilities sections above. If you don’t have a recent home appraisal, you can estimate your current home value by looking at your property taxes, the FHFA HPI Calculator or another home valuation tool.
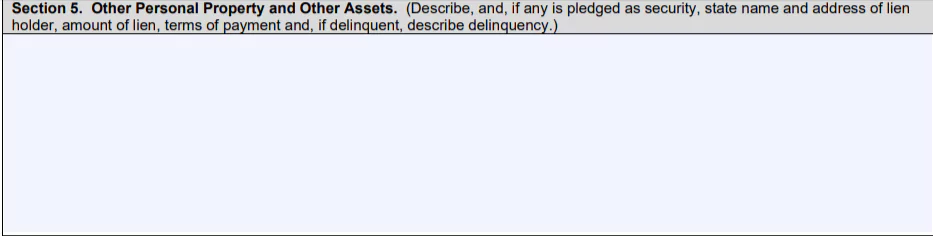
- Section 5: Describe the other assets you have, including boats, jewelry, collectibles, household goods, furniture, clothing and other valuables.
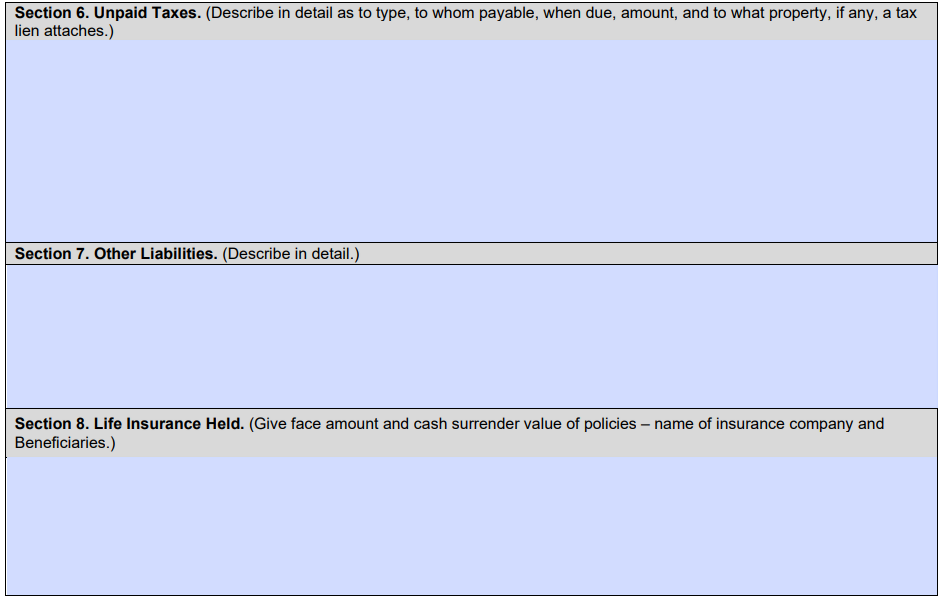
- Section 6: Describe any taxes you owe in detail, including who it’s owed to, the type of tax, the amount owed and when payment is due. If you owe property taxes, describe the property. If you have large tax bills, include documentation.
- Section 7: Describe any other liabilities in detail and attach bills or other documentation for particularly large amounts.
- Section 8: For each life insurance policy with a cash value component, list the name of the insurance company, the beneficiaries, the face amount and the cash surrender value.
9. Sign and submit
Finally, you will sign and date the form and enter your Social Security number. If you included any spousal assets on the form, your spouse will also need to sign and date the form and enter their Social Security number.
By signing, you’re acknowledging the information in the form is accurate. When you’re done, submit the form to the lender, Certified Development Company or surety company or agent processing your application.
What to do if you’re missing information
To fill out SBA Form 413, you’ll need to be prepared with bank account balances, real estate values and more. If you’re missing any of the information you need to complete the form, you may need to do some digging before you can submit your loan application.
Keep in mind that estimates are generally okay, but you should do your best to accurately represent the value of your assets. For example, if you don’t know the market value of your car or house, you may need to rely on online valuation tools to get an estimate, but don’t forget to explain how you calculated the value of each item.
If you have further questions about SBA Form 413, your local SBA district office may be able to help. You can also contact your lender directly.
Frequently asked questions
If you’re filling out SBA Form 413 and you have unpaid taxes, you’ll enter the total amount in the line for “unpaid taxes” in the “liabilities” section of the form. You’ll also describe them in detail in Section 6. You should not include anticipated taxes.
You should put the total balance across your credit card accounts in the line for “installment account (other)” under the “liabilities” section of SBA Form 413.
To determine your net worth on SBA Form 413, subtract your total liabilities from your total assets. The result is your net worth, which you’ll enter in the “liabilities” section of the form.
Compare business loan offers
Recommended Articles


